Artificial Intelligence: INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines designed to think, learn, and problem-solve like humans. It encompasses a variety of technologies, including machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, that allow machines to perform tasks traditionally requiring human intelligence. AI is transforming industries by automating processes, providing data-driven insights, and enhancing decision-making capabilities. As it continues to evolve, AI holds the potential to revolutionize the way businesses operate and individuals interact with technology.
Ease of Use
When choosing an artificial intelligence product, ease of use is one of the most important factors to consider. A user-friendly interface and an intuitive design can make a significant difference, especially for individuals or businesses new to AI technologies.
The best AI tools are designed to minimize the learning curve by offering clear navigation, helpful tutorials, and pre-built templates or models. These features make it easier for users to get started and accomplish tasks without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
For advanced users, ease of use also means efficient workflows and streamlined processes, enabling them to focus on innovation instead of troubleshooting complex interfaces. Products with well-organized dashboards and responsive designs perform better in this category, as they reduce frustration and improve productivity.
Features and Capabilities
When evaluating artificial intelligence products, features and capabilities play a crucial role in determining their suitability for specific needs. The versatility and functionality of an AI tool often define its value to businesses and individuals.
AI tools vary widely in what they offer. Some focus on automation, streamlining repetitive tasks like data entry, while others excel in advanced analytics, providing actionable insights from complex datasets. Key features to look for include natural language processing (NLP), machine learning capabilities, predictive analytics, and computer vision.
Additionally, many artificial intelligence products offer customizable solutions tailored to industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, and education. For example, AI-powered chatbots can enhance customer service, while image recognition tools are critical in sectors like security and manufacturing.
A robust AI product should also support integration with third-party applications and provide regular updates to enhance its functionality. Advanced features like real-time data processing, multi-language support, and detailed reporting further differentiate top-tier solutions.

Accuracy and Performance
Accuracy and performance are critical factors when selecting an artificial intelligence product. The effectiveness of AI tools directly depends on how reliably they can analyze data, make predictions, and perform tasks with minimal errors.
High-performing AI systems are built on robust algorithms and trained on extensive datasets to ensure precision. For example, AI used in speech recognition should accurately interpret different accents and dialects, while AI-powered recommendation engines must provide highly relevant suggestions.
Performance is also measured by the tool’s speed and consistency in delivering results. An efficient AI solution should process large volumes of data quickly without compromising accuracy. Tools that use adaptive machine learning models often improve their accuracy over time, making them ideal for long-term use.
Accuracy and performance are especially important in industries like healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems, where errors can have significant consequences. Evaluating performance metrics such as precision, recall, and response times can help you determine whether a tool meets your needs.
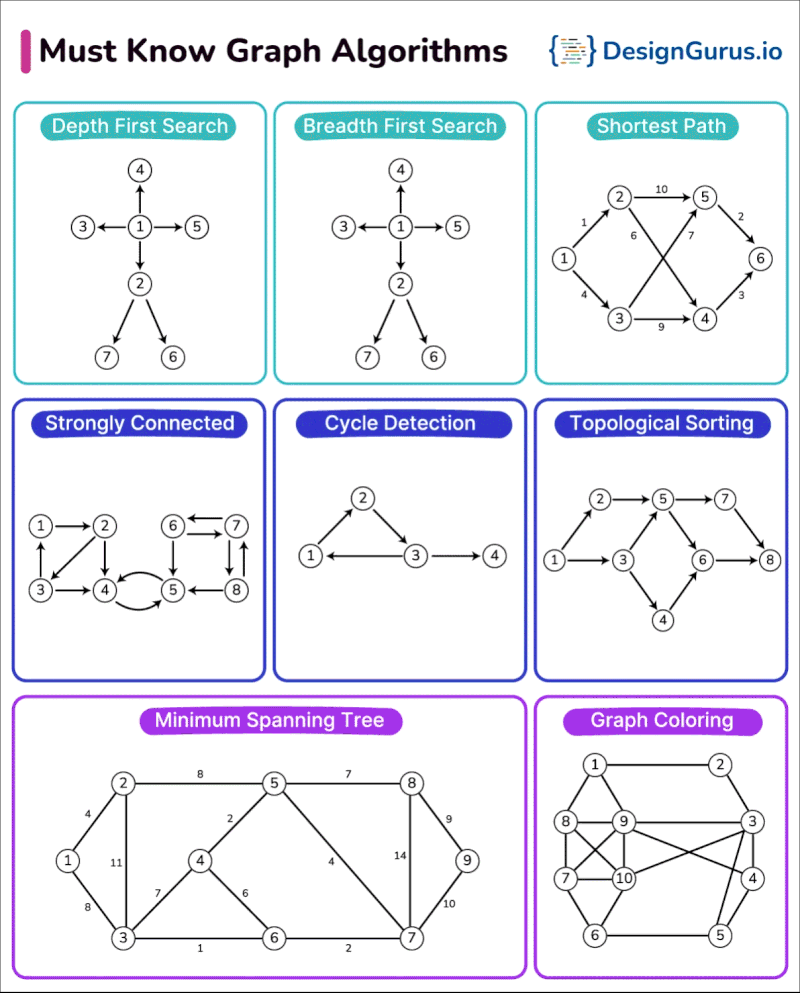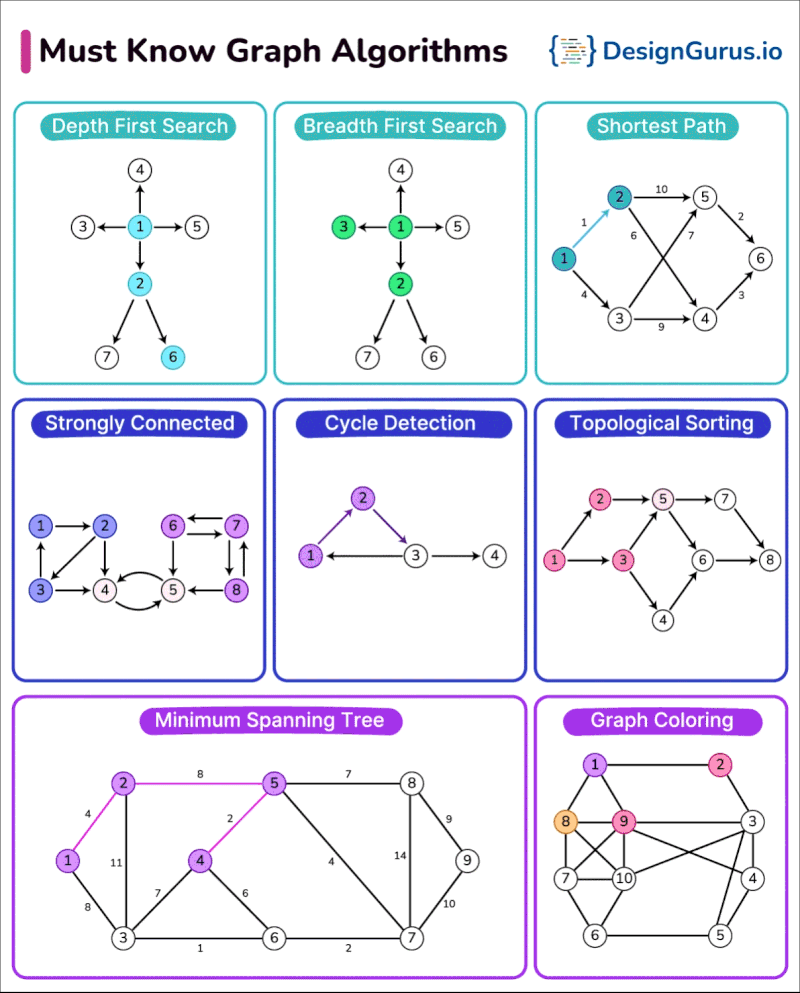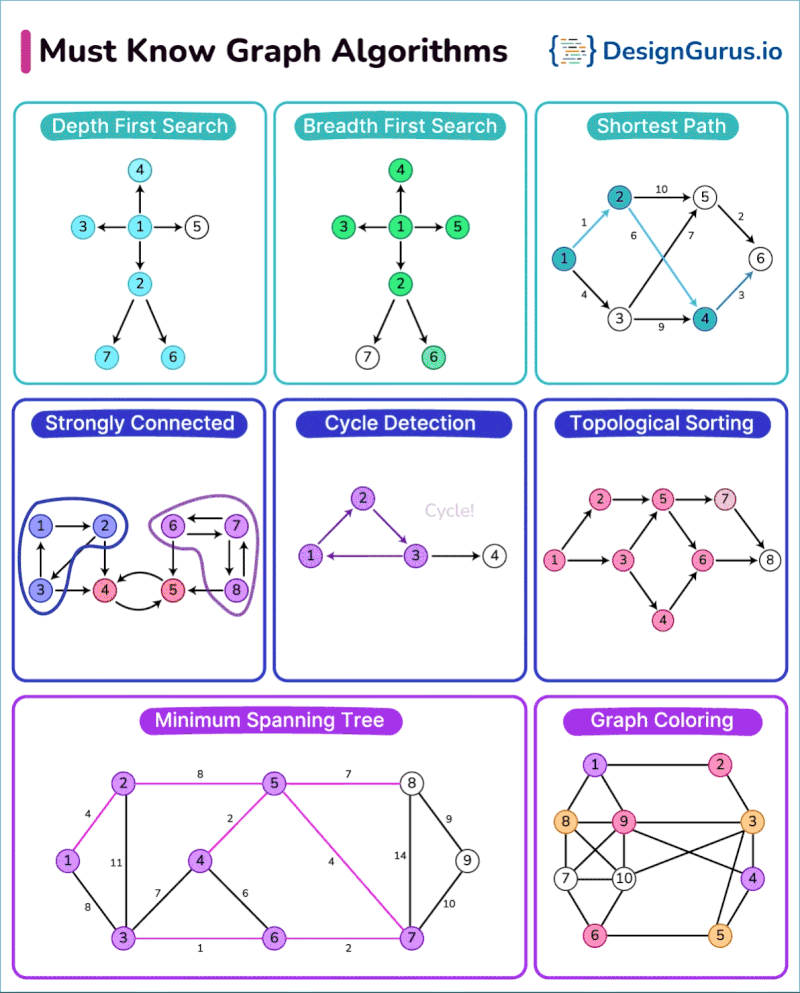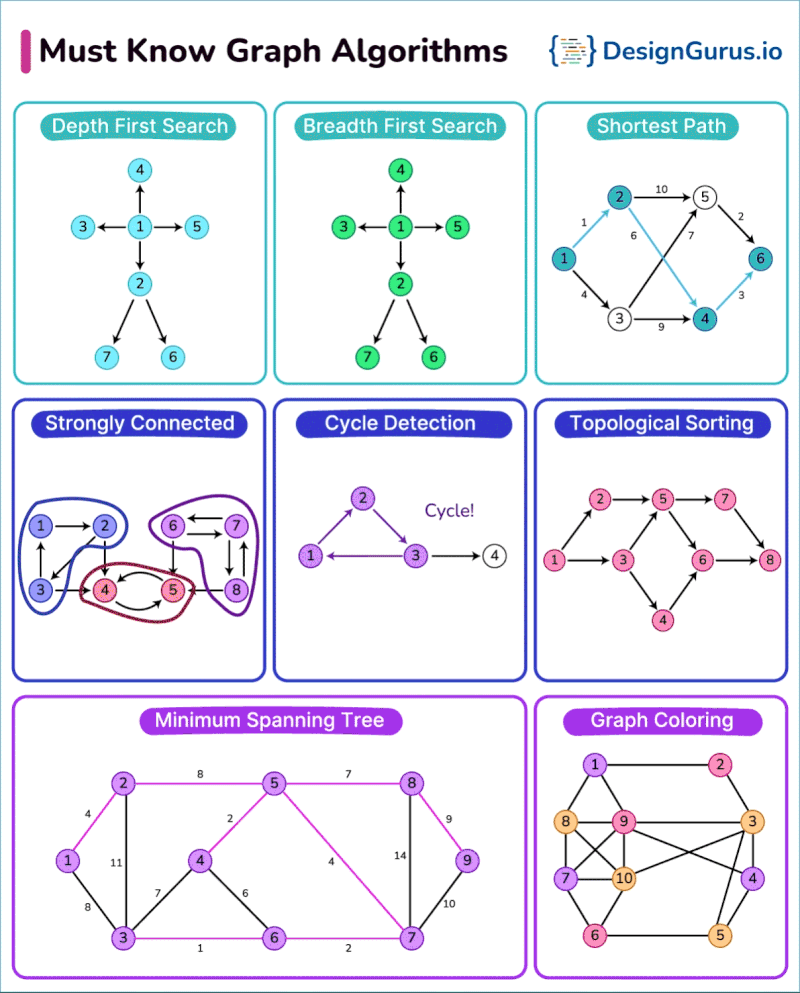
Pricing and Value for Money
Pricing and value for money are essential considerations when choosing an artificial intelligence product. The cost of AI tools can vary widely depending on the features offered, the complexity of the technology, and the intended use cases. It’s crucial to evaluate whether the benefits provided by the tool justify its price.
Most AI products fall into one of three pricing models:
- Subscription-based pricing – Common for SaaS AI tools, where users pay a recurring fee for access.
- Pay-as-you-go – Ideal for users who require flexibility, as you only pay for what you use.
- One-time purchase – A flat fee for perpetual access, typically seen in simpler or less frequently updated tools.
When assessing value for money, consider not only the upfront costs but also any hidden expenses such as integration fees, training costs, or premium support packages. Compare pricing tiers to identify which level provides the most useful features for your budget.
Some AI tools offer free trials or freemium versions, making it easier to test the product before committing. Additionally, many tools designed for small businesses or startups provide affordable entry-level options with scalable features for future growth.

Customer Support
Customer support is a vital factor to consider when evaluating artificial intelligence products. No matter how advanced or feature-rich an AI tool may be, users will inevitably encounter questions or issues that require assistance. High-quality customer support can make a significant difference in ensuring a smooth user experience.
The best AI tools offer multiple channels for support, such as live chat, email, and phone support. Some also provide extensive documentation, including FAQs, user guides, and video tutorials, to help users resolve common problems on their own.
24/7 support is particularly valuable for businesses operating across multiple time zones, ensuring issues can be addressed promptly. Additionally, some providers offer dedicated account managers or priority support for premium users, which can be a significant advantage for enterprises with complex requirements.
When assessing customer support, it’s also essential to consider the quality of responses. Timely, knowledgeable, and helpful answers are hallmarks of excellent support teams. Checking user reviews or feedback can give insights into the reliability of a company’s support services.

AI Model and Technology
The AI model and technology behind an artificial intelligence product are critical aspects that determine its functionality and effectiveness. AI tools are powered by different models, each designed for specific tasks and use cases. Understanding the underlying technology can help users select the best solution for their needs.
AI models are typically based on one or more of the following approaches:
- Machine Learning (ML): ML models learn from data to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. Examples include recommendation systems and fraud detection tools.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subset of ML, deep learning uses neural networks to process complex data such as images, audio, and video. Common applications include image recognition and natural language processing (NLP).
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP focuses on understanding and generating human language, powering tools like chatbots, sentiment analysis, and translation services.
- Reinforcement Learning: This model trains AI through rewards and penalties to optimize decision-making, often used in robotics and autonomous systems.
In addition to the models, the technology stack—such as cloud-based platforms, GPU acceleration, and APIs—plays a key role in the product’s performance. Advanced AI tools often incorporate hybrid technologies that combine multiple models to achieve higher accuracy and versatility.
Selecting a product with the right AI model and technology ensures better alignment with your specific requirements, whether it’s real-time data analysis, image classification, or language understanding.

Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are top concerns when choosing an artificial intelligence product. As AI tools often handle sensitive data, ensuring that these tools follow strict security protocols and respect user privacy is essential.
AI products should implement robust security measures to protect data from breaches, unauthorized access, or cyberattacks. Common practices include encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and secure data storage. AI providers must comply with industry standards and regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S. These frameworks ensure that user data is processed transparently and securely.
Privacy features, such as data anonymization or consent management, are also important. Anonymization removes personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets, minimizing privacy risks. Additionally, AI tools should provide users with control over their data, allowing them to opt in or out of data collection or share data only for specific purposes.
Businesses should also inquire about the AI provider’s data retention policies. AI tools should not keep user data longer than necessary, and they should ensure secure deletion once the data is no longer required. A clear privacy policy outlining how data is handled and protected is a strong indicator of a trustworthy AI provider.

Speed and Efficiency
Speed and efficiency are critical factors when selecting an artificial intelligence product. AI tools are designed to process vast amounts of data, and how quickly and efficiently they do so can significantly impact user experience and business outcomes.
A high-performance AI tool should be able to deliver quick results, even when dealing with large datasets or complex tasks. Speed is particularly important in real-time applications, such as fraud detection, autonomous driving, or customer service chatbots, where delays can lead to missed opportunities or errors.
Efficiency refers to how well the AI product maximizes resources. An efficient AI tool can complete tasks with minimal computational power and energy consumption, ensuring faster processing times and lower operational costs. Tools that use optimized algorithms or run on cloud-based infrastructures with GPU acceleration tend to perform better in terms of both speed and efficiency.
AI tools with poor speed or inefficient processing can lead to bottlenecks in workflows, causing frustration and delays. Therefore, when choosing an AI product, it’s essential to consider the processing time and the tool’s ability to handle increasing workloads over time.
Pros of Using Artificial Intelligence
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks
AI can automate mundane and repetitive tasks, saving time and reducing human error. This increases overall efficiency and allows employees to focus on higher-value work. - Data Analysis and Insights
AI can process and analyze vast amounts of data quickly, providing valuable insights that would be time-consuming or even impossible for humans to gather. This is especially useful in sectors like healthcare, finance, and marketing. - 24/7 Availability
Unlike human workers, AI systems can operate around the clock without breaks. This is especially beneficial for tasks such as customer support (e.g., chatbots) or monitoring systems. - Improved Decision-Making
AI helps businesses make data-driven decisions by providing predictive analytics and detailed reports. It can detect patterns and trends that humans might miss, improving strategic planning. - Personalization
AI-powered tools can tailor experiences or recommendations based on user behavior and preferences, leading to better customer satisfaction and increased sales. - Scalability
AI tools are scalable, meaning they can grow alongside a business. As the company expands or the amount of data increases, AI systems can handle the greater load without significant increases in cost or resources.
Cons of Using Artificial Intelligence
- High Initial Costs
Implementing AI tools often involves a significant upfront investment. This can include software, hardware, and the cost of training employees to use the technology effectively. - Job Displacement
While AI can automate many tasks, it may lead to job displacement, especially for roles involving repetitive work. This can be a concern for employees whose tasks are replaced by AI systems. - Complexity in Implementation
The process of integrating AI tools into existing workflows can be complex and time-consuming. It often requires specialized knowledge or technical expertise to ensure proper implementation. - Data Privacy Concerns
AI tools often require large amounts of data to function effectively. This raises concerns about data privacy and security, especially when handling sensitive or personal information. - Bias and Errors
AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the data contains biases or inaccuracies, AI can make biased or incorrect decisions, leading to unintended consequences. - Dependence on Technology
Over-reliance on AI can make businesses vulnerable if the technology fails or malfunctions. It’s crucial to have human oversight and contingency plans in place to manage these risks.

